,,
The internet of things, or IoT, is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals, or people that are provided with unique identifiers (UID’s) and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.
IoT can be used in every application like an automobile that has built-in sensors to alert the driver when tire pressure is low or any other natural or man-made object that can be assigned an Internet Protocol (IP) address and is able to transfer data over a network.
Increasingly, organizations in a variety of industries are using IoT to operate more efficiently, better understand customers to deliver enhanced customer service, improve decision-making, and increase the value of the business. IoT has a brighter future ahead. In 2018, there are only 7B IoT devices in the market. But in 2025, there will be more than 64B Internet of Things devices available globally
How IoT works – IoT Internet Of Things:
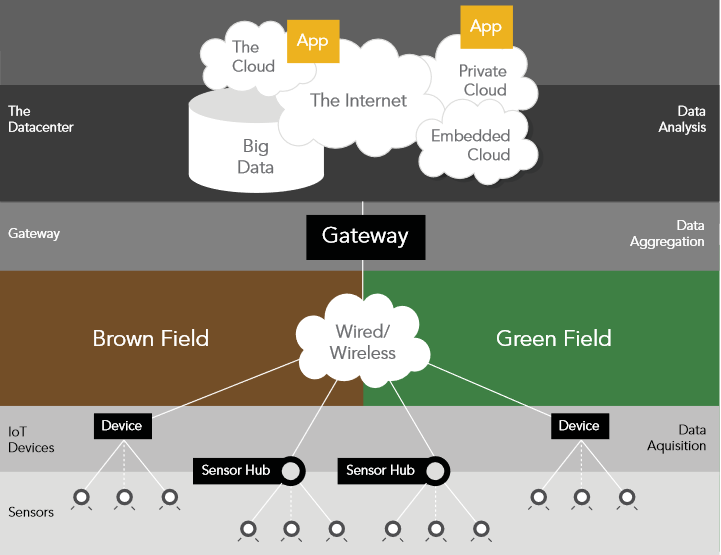
The components of IoT are sensors, connectivity, data processing, and user interface. An IoT ecosystem consists of web-enabled smart devices that use embedded systems, such as processors, sensors, and communication hardware, to collect, send, and act on data they acquire from their environments. IoT devices share the sensor data they collect by connecting to an IoT gateway or other edge device where data is either sent to the cloud to be analyzed or analyzed locally. Sometimes, these devices communicate with other related devices and act on the information they get from one another. The devices do most of the work without human intervention, although people can interact with the devices — for instance, to set them up, give them instructions, or access the data.
The connectivity, networking, and communication protocols used with these web-enabled devices largely depend on the specific IoT applications deployed.
IoT can also make use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to aid in making data collecting processes easier and more dynamic. Can IoT work without Internet? Yes, it can work in some cases.
You can get an idea of how IoT works by seeing this video in the below link:
IoT benefits to organizations:
Most organizations have already implemented technologies—such as instrumentation, supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA), and asset management or computerized maintenance management systems—to provide near-real-time visibility of their processes and operations. So what value will the Internet of Things (IoT) add to existing technology investments? The short answer is a lot, though the specifics depend on the industry. It can also generate works in cloud companies.
The internet of things offers several benefits to organizations. Some benefits are industry-specific, and some are applicable across multiple industries. Some of the common benefits of IoT enable businesses to:
- monitor their overall business processes;
- improve the customer experience (CX);
- save time and money;
- enhance employee productivity;
- integrate and adapt business models;
- make better business decisions; and
- generate more revenue.
IoT wireless technologies:
There is a number of technologies to be used in IoT for its usability and to increase its area of implementation. Here is a detailed view of one of the technology LPWAN and its sub-technologies.
 1.LPWAN:
1.LPWAN:
LPWAN’s are a new phenomenon in IoT. By providing long-range communication on small, inexpensive batteries that last for years, this family of technologies is purpose-built to support large-scale IoT networks sprawling over vast industrial and commercial campuses. LPWAN from 5 to 30 km in different environmental conditions. LPWAN is not a singular technology, but rather a term used to describe any wireless technology that achieves a long operating range while maintaining low power requirements.
LPWAN is low-power wide-area network also known as LPWA Network — is a new type of radio technology used for wireless data communication in different Internet of things applications and Machine to machine(M2M) solutions. Key features inherent in the technology are the long-range of communication, low bit rate, and small power budget of transmission.
Some of the evolution’s and sub-technologies of LPWAN are SigFox, LoRa, Symphony Link, Weightless, NB-IoT, and LTE-M.
IoT Internet Of Things is an emerging technology to ease human activities, it can be used in every field of use to decrease the difficulty of work. IoT is used in home application like mobile activated lights, car, door, wearables, and home appliances, it is also used in industries and companies for sensor-activated devices and fire alarms. Apart from this IoT is used in a variety of fields like communication field, medical field like detecting stroke cause and giving alert notification and in technology fields it is used by technology giants like Google and Amazon in their products Google home vs Alexa. App creators are using IoT as part of their apps to increase their advancement.
CONCLUSION:
The Internet of Things is closer to being implemented than the average person would think. Most of the necessary technological advances needed for it have already been made, and some manufacturers and agencies have already begun implementing a small-scale version of it. It can change the economy to a better stage and help to decrease the workload and can be used to increase the number of technologies to be used day-by-day. The near future is all about technology so knowing about IoT will help to adapt ourselves to that technology.